Dive into the enchanting world of foraging, where every leaf and berry tells a story of survival, tradition, and the untamed beauty of nature.
Embrace this age-old practice to connect deeply with the earth, nourish your body, and awaken your sense of adventure.
Table of Contents
Key Takeways:
- Start your foraging journey with easily identifiable plants and mushrooms, expanding your knowledge and skills gradually.
- Embrace sustainable foraging practices to protect and respect the natural environment.
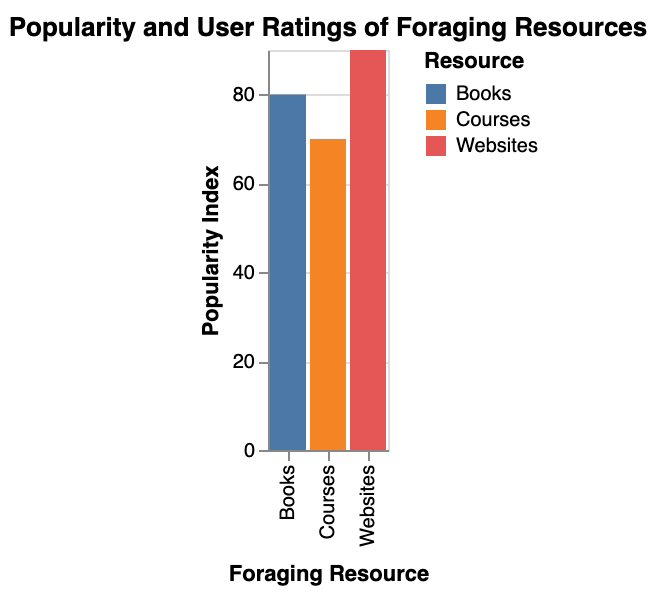
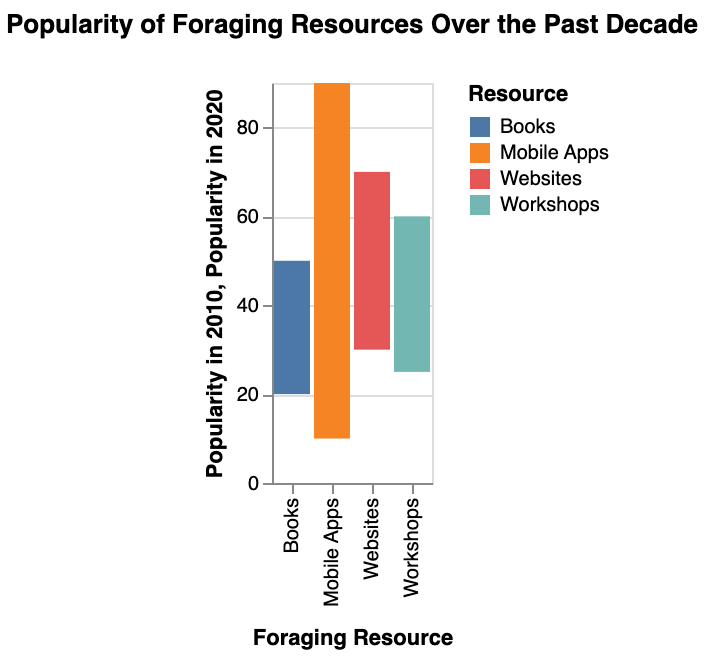
- Utilize various resources such as books, online courses, and guided tours to enhance your foraging expertise.
- Learn to properly identify, harvest, and prepare wild edibles to safely enjoy the bounty of nature.
Identifying Edible Wild Plants and Mushrooms

Starting Your Foraging Journey
When starting to forage for wild food, it’s crucial to recognize the distinction between edible and poisonous plants.
A good field guide specific to your region is a forager’s best friend for correctly identifying wild edibles.
Remember, not all wild plants are meant for harvest; some may be medicinal, while others might be considered weeds.
| Category | Characteristics | Uses | Example Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edible Plants | Safe for consumption, often rich in nutrients | Food, cooking, nutrition | Spinach, Apples, Carrots |
| Medicinal Plants | Possess medicinal properties, used for health benefits | Herbal remedies, treatment of ailments | Echinacea, Aloe Vera, Ginseng |
| Weed Plants | Often considered invasive or undesirable, can have medicinal properties | Some used for herbal remedies | Dandelion, Stinging Nettle, Purslane |
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Identifying Wild Edibles
One common mistake many novice foragers make is relying solely on visual cues when identifying wild edibles.
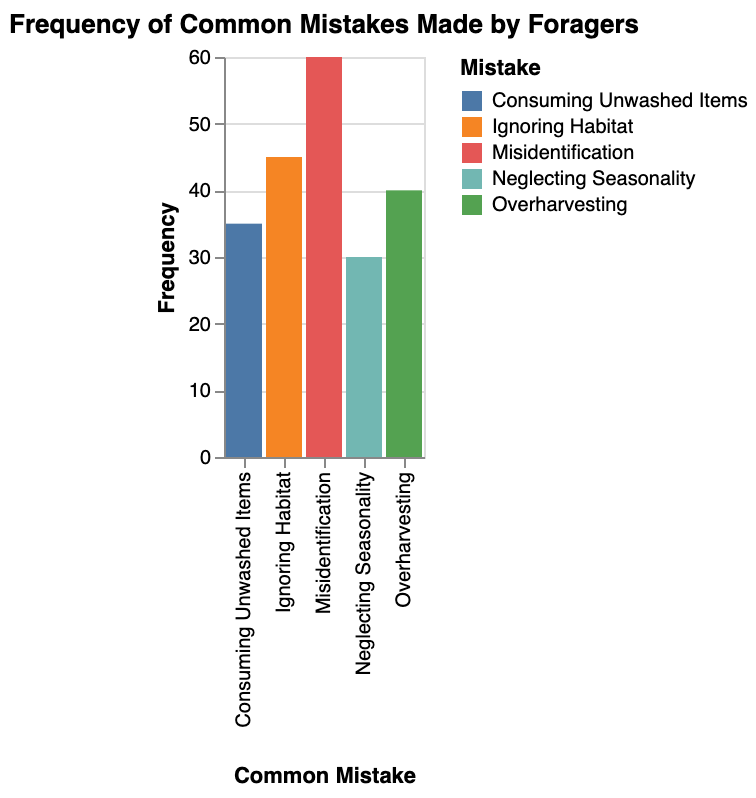
Remember that some poisonous plants may look similar to edible plants, so solely trusting your eyes can be risky.
Another pitfall is failing to cross-reference multiple sources when confirming the edibility of a wild plant.
Essential Foraging Tools for Every Forager

Gear up with the Basics
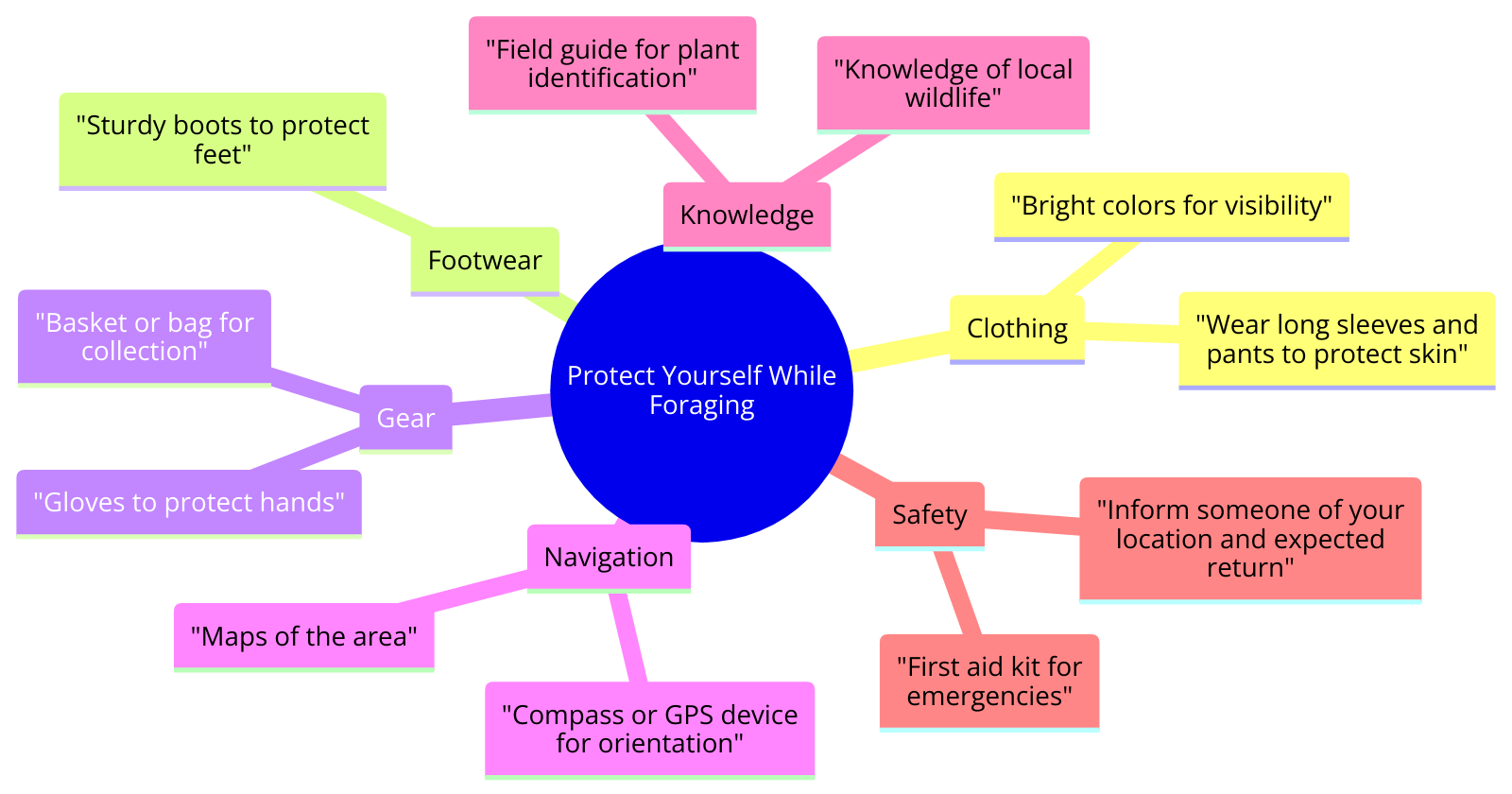
When heading out to search for wild edibles, there are a few essential foraging tools that can make your experience more productive and safe.
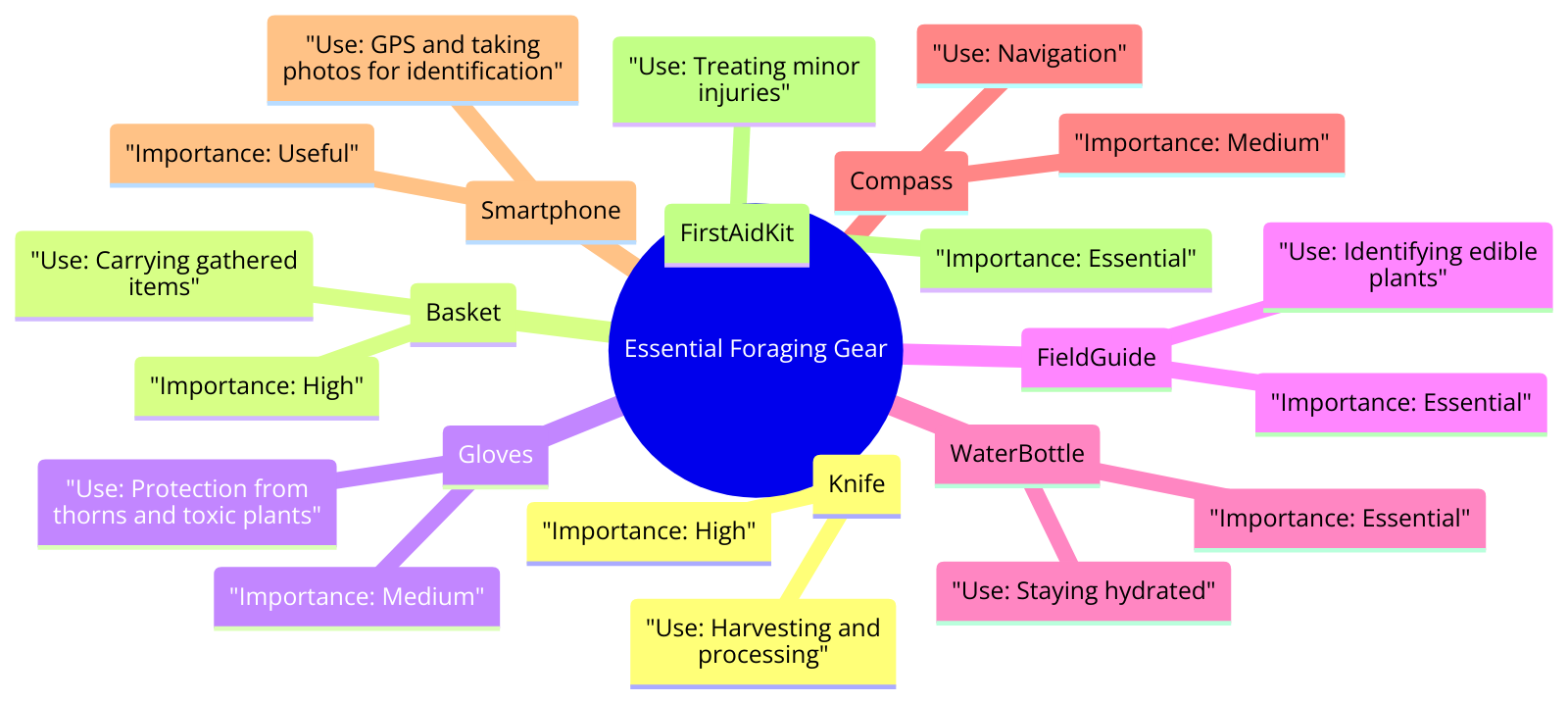
A good pair of sturdy boots is a must, especially when navigating uneven terrain.
Carry a sharp knife for cutting through vegetation and a foraging basket to collect your finds.
Consider bringing a guide to foraging to help you identify wild plants accurately.
Safety First
In the realm of foraging, safety is key.
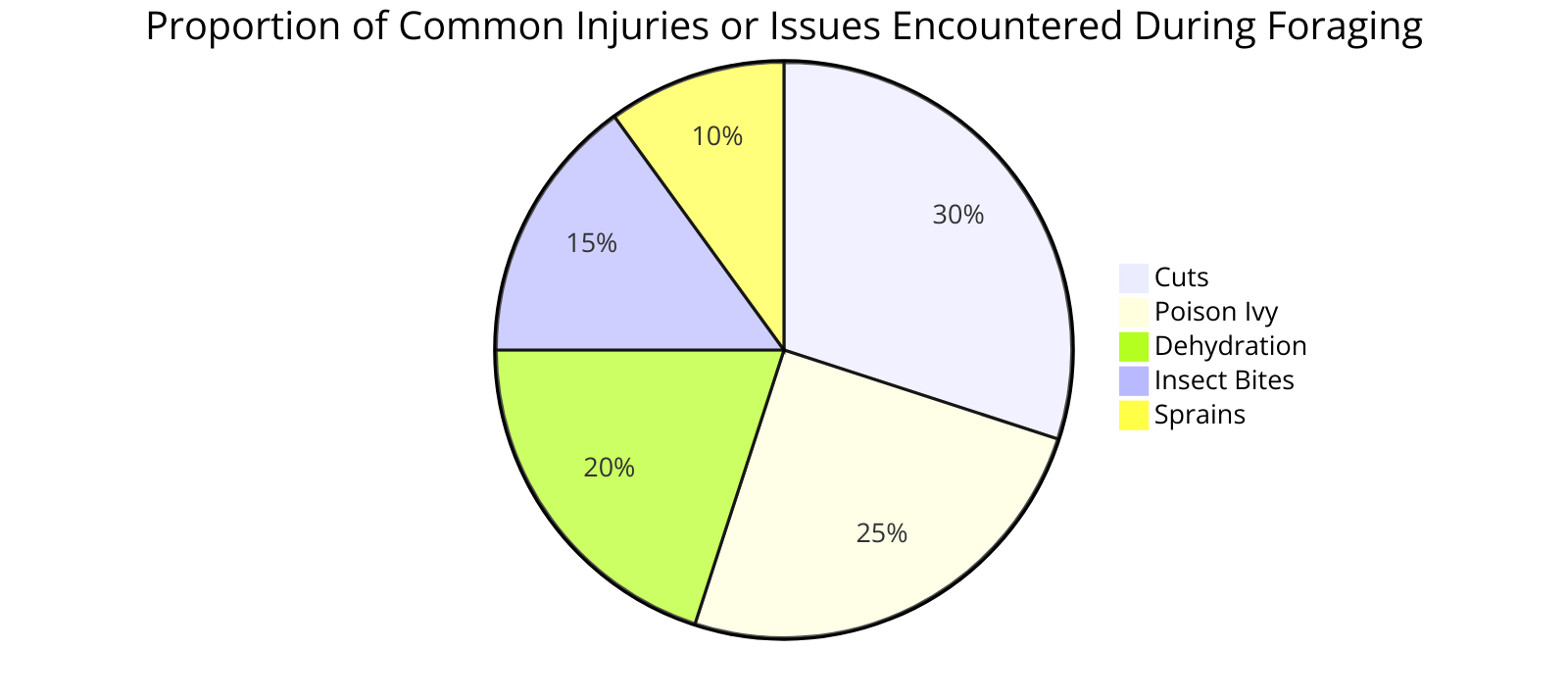
Always carry a bottle of water to stay hydrated while out in the wild.
Equip yourself with a pair of gloves to protect your hands from potential poisonous plants like hemlock.
Additionally, a magnifying glass can come in handy when inspecting tiny details that help differentiate edible and medicinal plants from toxic ones.
Sustainable Harvesting Practices for Wild Edibles

Foraging Mindfully
When venturing out to gather wild edible plants and fungi, it’s crucial to do so with respect for nature and sustainability in mind.
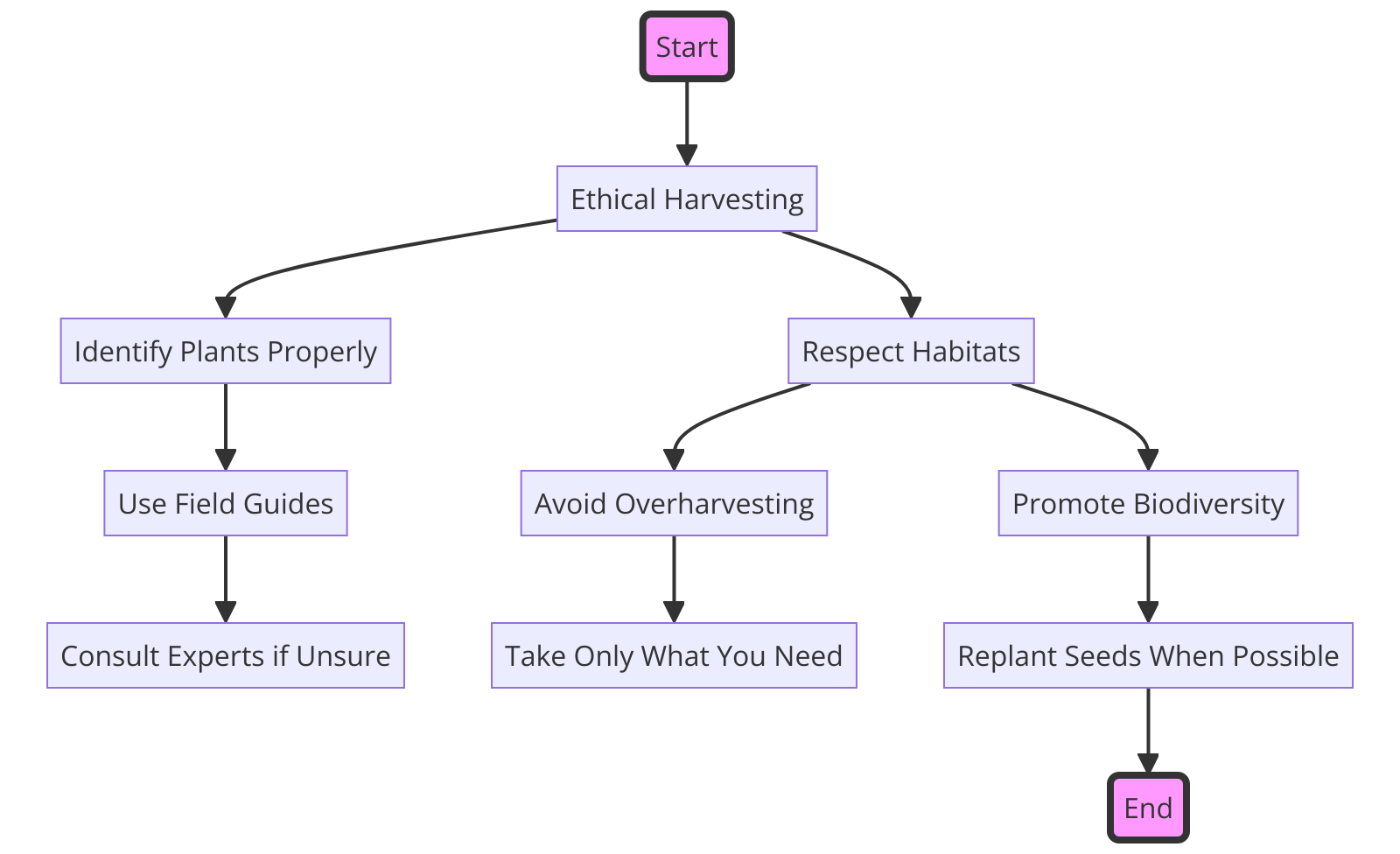
Building foraging skills is not only about recognizing what plants and fungi are safe to consume but also understanding how to harvest them responsibly.
| Practice | Sustainable Examples | Non-Sustainable Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Harvesting invasive species | Removal of invasive plants, reducing ecological impact | Overharvesting invasive species, disrupting ecosystems |
| Selective harvesting | Gathering only abundant species, allowing for natural replenishment | Harvesting rare or endangered species, depleting populations |
| Seasonal harvesting | Collecting plants only during their peak seasons | Harvesting plants out of season, affecting reproduction and growth |
| Regenerative harvesting methods | Gathering plant parts that promote regrowth, such as leaves or berries | Removing entire plants or roots, preventing regeneration |
Foraging Safely
When delving into the world of online foraging or exploring the wild for plants and fungi, prioritizing safety is paramount.
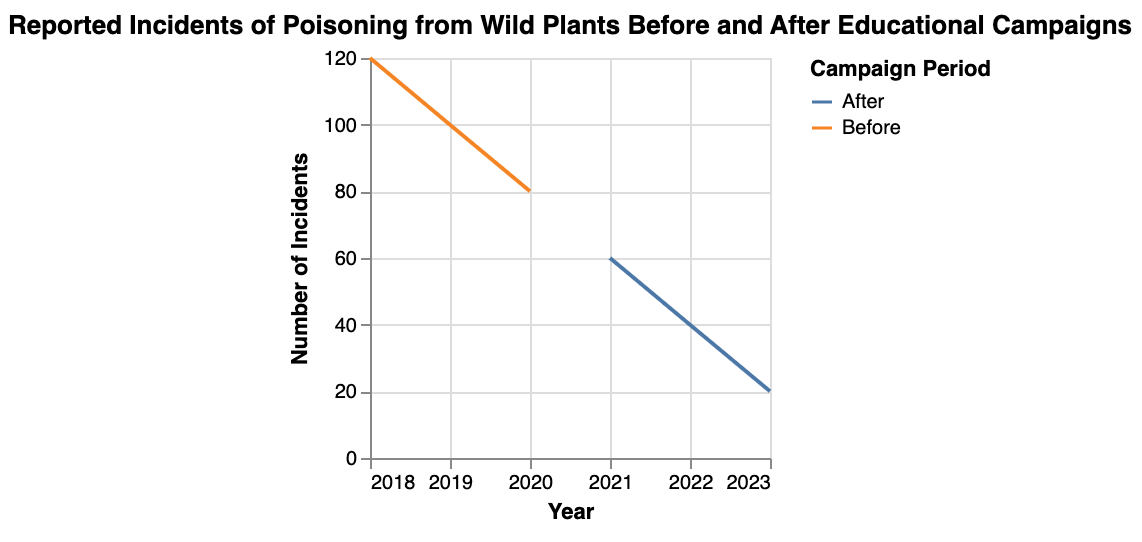
To forage safely and avoid unintended encounters with poisonous plants, it’s essential to stay informed and cautious.
Whether you’re new to the practice or a seasoned forager, always remember to take necessary precautions when foraging for wild edibles.
The Legalities of Foraging: Laws and Ethics

Navigating the Ethics and Laws of Foraging
Before setting off to harvest wild treasures from nature, be sure to research the regulations governing foraging in your area.
Understanding the legalities of foraging ensures that you are respecting both the environment and any restrictions in place to protect vulnerable plant populations.
By adhering to these laws and ethical guidelines, you can enjoy the bounty of nature responsibly while safeguarding the sustainability of wild plant populations.
| Region/Country | Allowed Practices | Protected Plants | Harvesting Limits |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Limited foraging in public lands, regulated by state laws | Endangered species, sensitive ecosystems | Harvesting permits, seasonal restrictions |
| United Kingdom | Permitted foraging in public spaces with landowner consent | Protected species under Wildlife and Countryside Act | Restrictions on certain areas, permits may be required |
| Australia | Limited foraging in national parks and protected areas | Native plants and species, conservation areas | Permit requirements, restrictions on protected species |
| Canada | Permitted foraging in Crown lands, subject to regulations | Endangered or threatened species, protected habitats | Harvesting quotas, licensing requirements |
Preparing and Preserving Your Foraged Finds

Feeling Intimidated by Where to Start
If you have the idea of foraging but feel intimidated about diving into the wild world of wild mushrooms and plants, consider taking an online foraging course.
These courses provide valuable insights into identifying edible species and navigating wild places to forage safely and ethically.
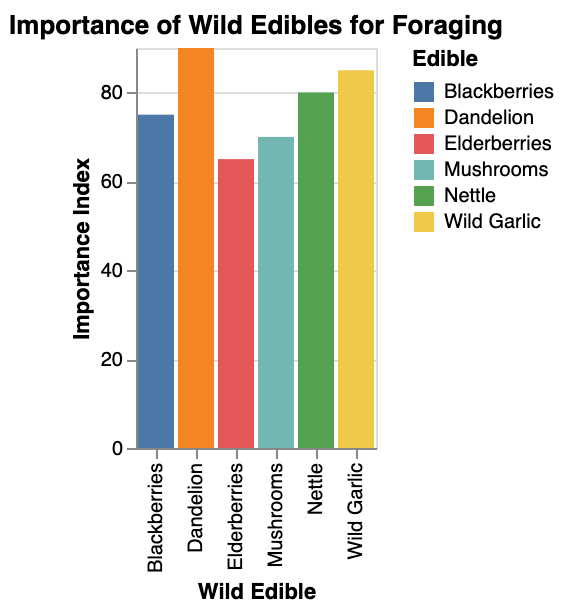
A good rule of thumb is to start with plentiful and easy-to-identify edibles like wild garlic and gradually expand your repertoire as you gain confidence.
Exploring Resources for Foraging Guidance
For those who plan to forage, utilizing resources such as the best books on foraging can be immensely beneficial.
By equipping yourself with the right knowledge, you can embark on your foraging journey with more confidence and a deeper appreciation for the bounties of nature.
Foraging Safety: Avoiding Poisonous Plants

Identifying Poisonous Plants: Tips for Beginners
When you’re new to foraging, it’s best to start with familiar, abundant wild edibles like wild blackberries before venturing into less-known territory.
Understanding how to differentiate between safe and harmful plants is just as important as recognizing the desirable ones.

Before heading out on your next foraging outing, brush up on your identification skills to ensure a successful and safe experience.
| Plant | Edible Features | Poisonous Features |
|---|---|---|
| Wild Garlic | Onion-like smell, hollow stems, flat leaves | Lack of onion smell, toxic bulbs |
| Water Hemlock | White flowers clustered in umbels, ridged stems | Tubers resembling parsnips, foul odor |
| Wild Strawberries | White flowers with five petals, red berries | Yellow or white berries, bitter taste |
| Deadly Nightshade | Purple bell-shaped flowers, shiny black berries | Entire plant is toxic, including berries |
| Common Morel | Distinct honeycomb cap, hollow stem | Lack of distinct cap, non-hollow stem |
| Poison Ivy | Leaves grouped in clusters of three, reddish in fall | Leaves are shiny with smooth edges, clusters of three |
Ensuring a Safe Foraging Experience
To stay safe when gathering plants and fungi, always prioritize your well-being.
If you’re new to this activity, it’s crucial to become comfortable foraging in your environment and confident in your abilities.
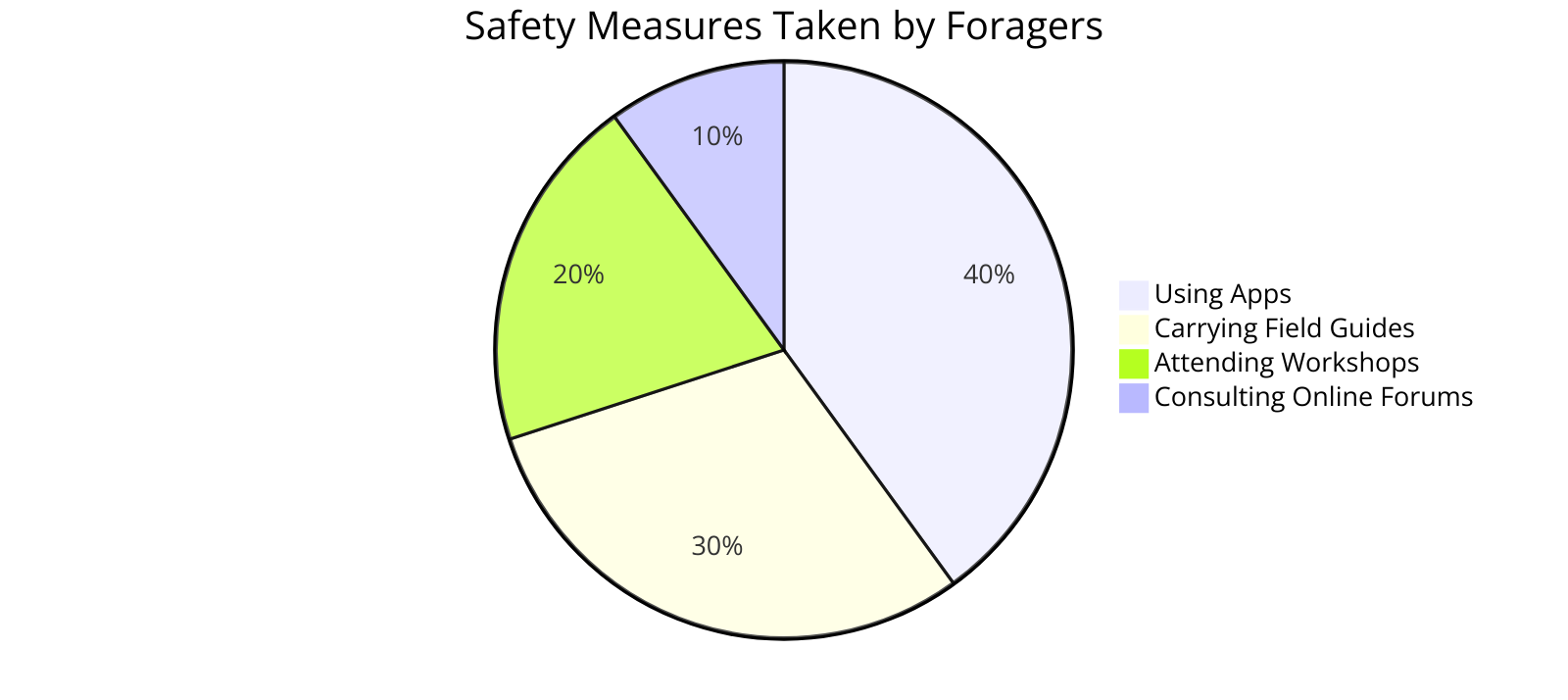
Expanding Your Foraging Skills

Exploring New Territories
When it comes to expanding your foraging skills, gaining confidence is essential.
One way to do this is by gathering wild plants in different areas.
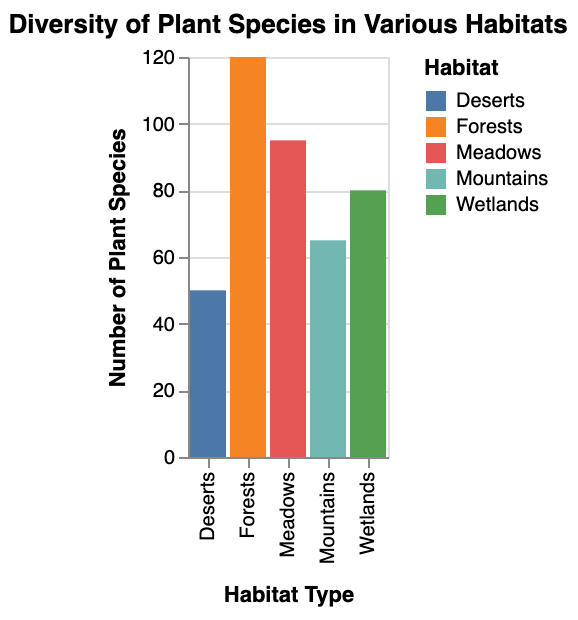
Exploring new territories can introduce you to a variety of wild plants you may not have encountered before.
Consider venturing into forests, meadows, and wetlands to discover a wide range of edible species.
Always remember to follow a guide to identifying plants and mushrooms to ensure you use foraging safely and effectively.
Experimenting with Medicinal Finds
Expanding your foraging skills also involves exploring the medicinal properties of plants.
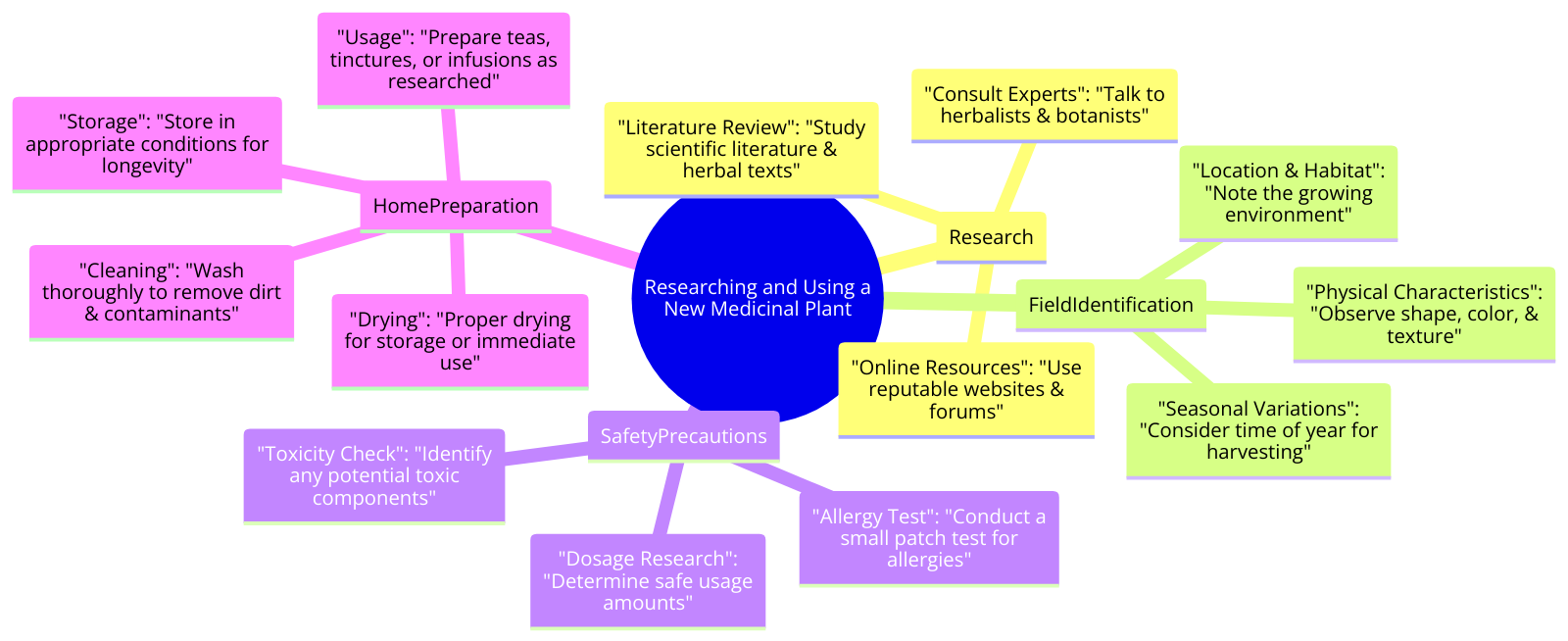
Many wild plants and mushrooms have been used for centuries in herbal and fungal medicines.
Once you have a good understanding of foraging safety, you can begin to identify species with medicinal benefits.
| Plant/Fungus | Health Benefits | Preparation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Echinacea | Boosts immune system, reduces cold symptoms | Brew dried leaves into tea, take as tincture |
| Ginger | Anti-inflammatory, aids digestion | Grate fresh root into tea or add to cooking |
| Turmeric | Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant properties | Add powdered root to smoothies or curries |
| Garlic | Antimicrobial, cardiovascular support | Crush cloves and add to food, or take as capsules |
| Elderberry | Immune support, cold and flu relief | Simmer dried berries into syrup or tea |
| Reishi Mushroom | Immune modulation, stress relief | Brew dried slices into tea, take as tincture |
| Lavender | Calming, sleep aid | Steep dried flowers into tea, use in aromatherapy |
| Chamomile | Relaxation, digestion aid | Brew dried flowers into tea, use in bath or as compress |
Learn how to properly prepare and preserve these plants for future use.
Start by focusing on a single plant or mushroom and delve deeper into its medicinal uses.
More Resources:





