Embarking on the journey of creating a survival garden is not just a venture into self-sufficiency; it’s an act of resilience and foresight.
By selecting the right crops and designing an efficient layout, you can ensure a steady supply of food regardless of what the future holds.
Table of Contents
Planning Your Survival Garden: A Gardener’s Blueprint

Choosing the Right Crops
When planning your survival garden, consider growing a mix of vegetables that are essential for sustenance and suitable for your region’s growing season.
Focus on crops that are easy to grow yet provide high nutritional value, such as winter squash.
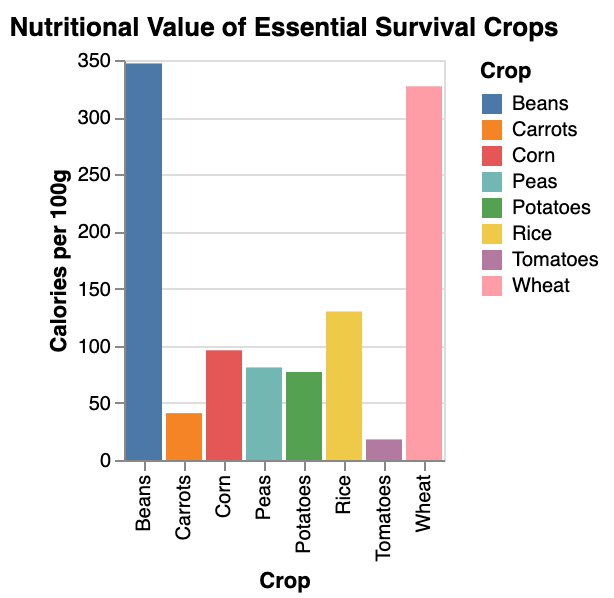
Identify the vegetables you need to grow to sustain yourself in a survival situation.
| Vegetable | Ease of Growth | Nutritional Value | Growing Season Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Moderate | High in vitamin C, potassium, and antioxidants | 60-100 days |
| Lettuce | Easy | Good source of vitamins A, K, and folate | 30-60 days |
| Spinach | Easy | High in iron, vitamins A and C, and antioxidants | 30-50 days |
| Carrots | Moderate | High in beta-carotene, fiber, and vitamin K | 70-80 days |
| Cucumbers | Easy | Hydrating, good source of vitamins K and C | 50-70 days |
| Peppers | Moderate | High in vitamin C, antioxidants, and capsaicin | 60-90 days |
| Zucchini | Easy | Low in calories, good source of vitamin C and potassium | 50-60 days |
| Green Beans | Easy | Good source of fiber, protein, and vitamins A and C | 50-70 days |
| Broccoli | Moderate | High in vitamins K and C, fiber, and antioxidants | 60-100 days |
| Onions | Easy | Good source of vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants | 80-100 days |
| Potatoes | Moderate | High in potassium, vitamins C and B6, and fiber | 70-120 days |
“The key to a resilient survival garden lies not just in the selection of crops, but in understanding the harmony between the soil and the seasonal cycles,”
says Dr. Linda Greene, a noted agricultural scientist
Mapping Out Your Garden Bed
Map out your garden bed to determine where each crop will be planted, ensuring you maximize yield and space efficiency.
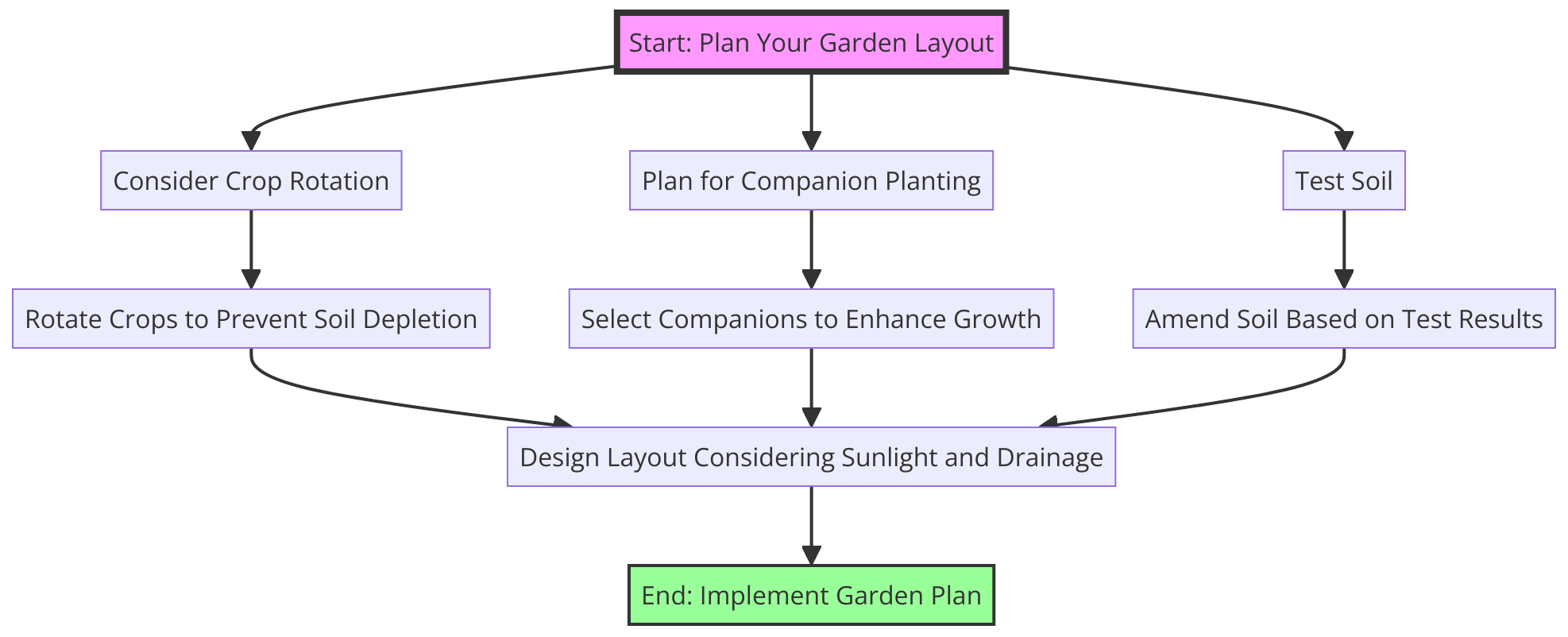
Consider companion planting to help plants thrive and deter pests naturally.
Strategically plan for harvest times to ensure a continuous supply of fresh food from your garden.
As a gardener, always have a backup plan for unpredictable factors that may affect your food source.
Essential Crops for a Survival Garden: What You Need to Grow

Choosing the Right Crops
When planning your survival garden, it’s crucial to select crops that will thrive in your garden space and provide essential nutrients.
Root vegetables, such as carrots and potatoes, are excellent choices as they are nutrient-dense and can be stored for extended periods.
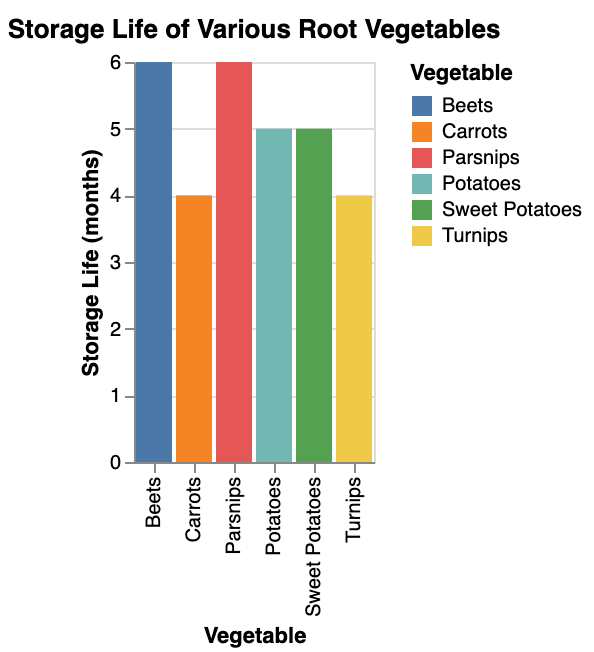
Consider medicinal plants like chamomile and peppermint, which not only have healing properties but also add diversity to your garden.
| Medicinal Plant | Health Benefits | Compatibility with Survival Crops |
|---|---|---|
| Aloe Vera | Soothes burns, aids digestion, boosts immune system | Compatible with most crops |
| Lavender | Relieves stress and anxiety, promotes sleep | Compatible with many crops |
| Peppermint | Relieves nausea, aids digestion, alleviates headaches | Compatible with most crops |
| Chamomile | Calms nerves, promotes sleep, aids digestion | Compatible with most crops |
| Garlic | Boosts immune system, lowers blood pressure | Compatible with most crops |
| Ginger | Aids digestion, reduces nausea and inflammation | Compatible with most crops |
Remember to save seeds from your best-performing plants for future planting to ensure a sustainable food source.
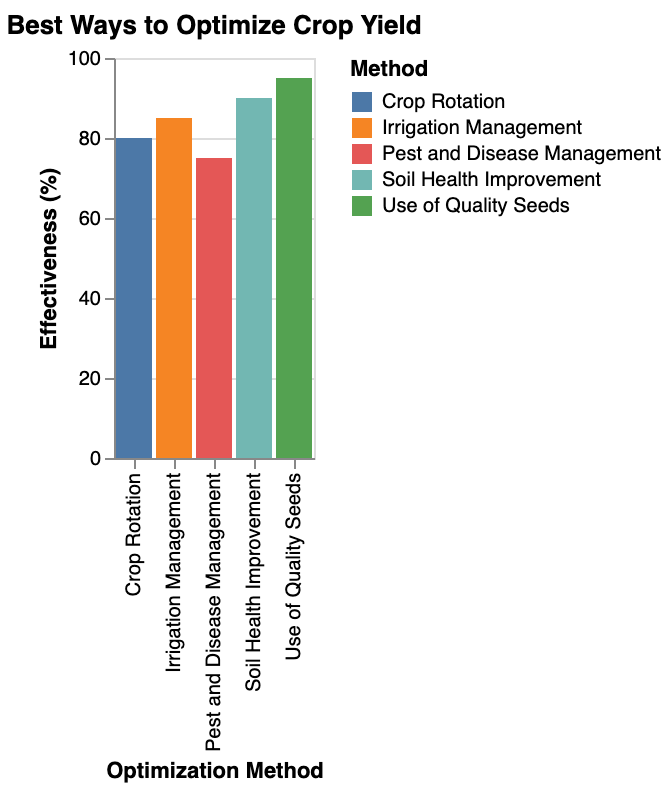
Maximizing Yield in Limited Spaces
In a square foot garden or when container gardening, optimizing garden area is key.
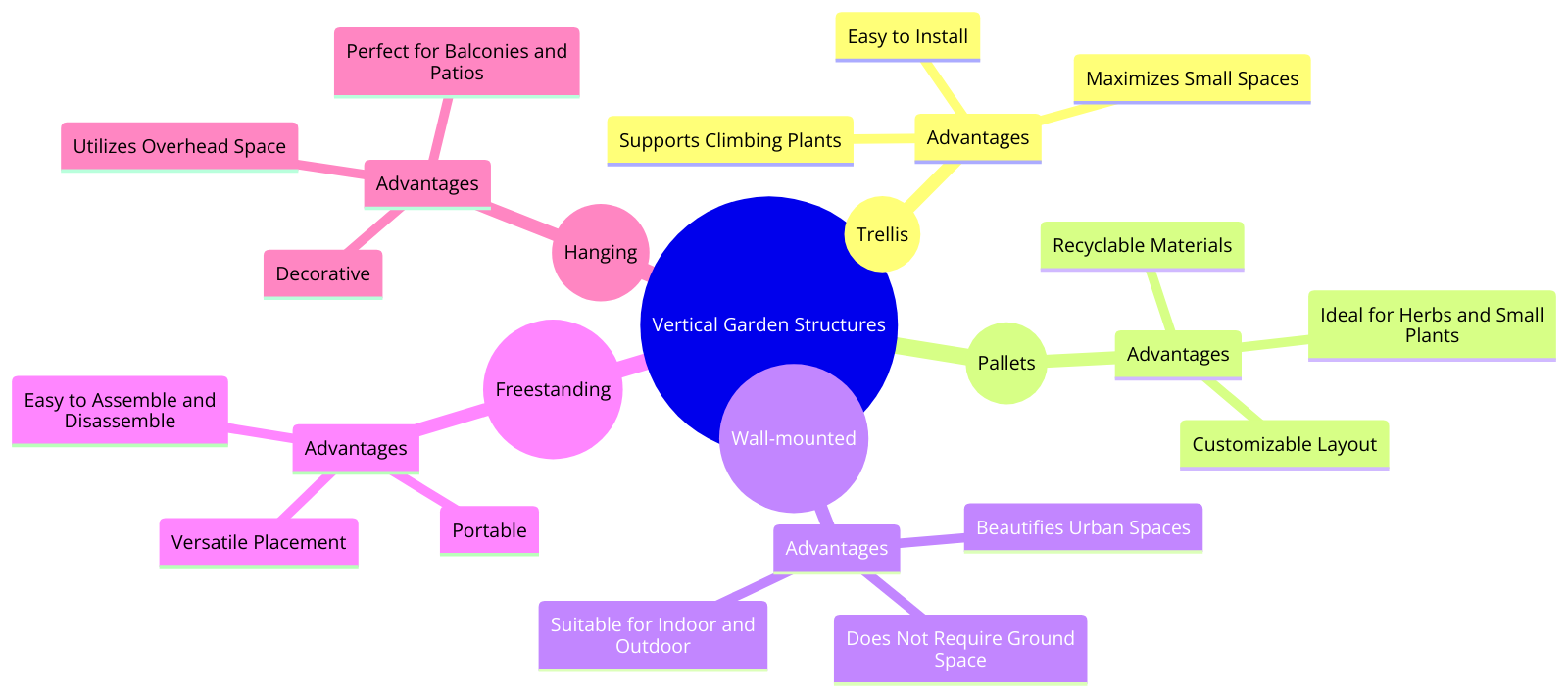
If you want to grow a variety of crops in a limited garden space, consider succession planting to ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce.
To make the most of your survival garden layout, interplant compatible crops and utilize vertical space with trellises for climbing plants.
Seed saving is essential in these setups to maintain a continuous harvest without relying on external sources.
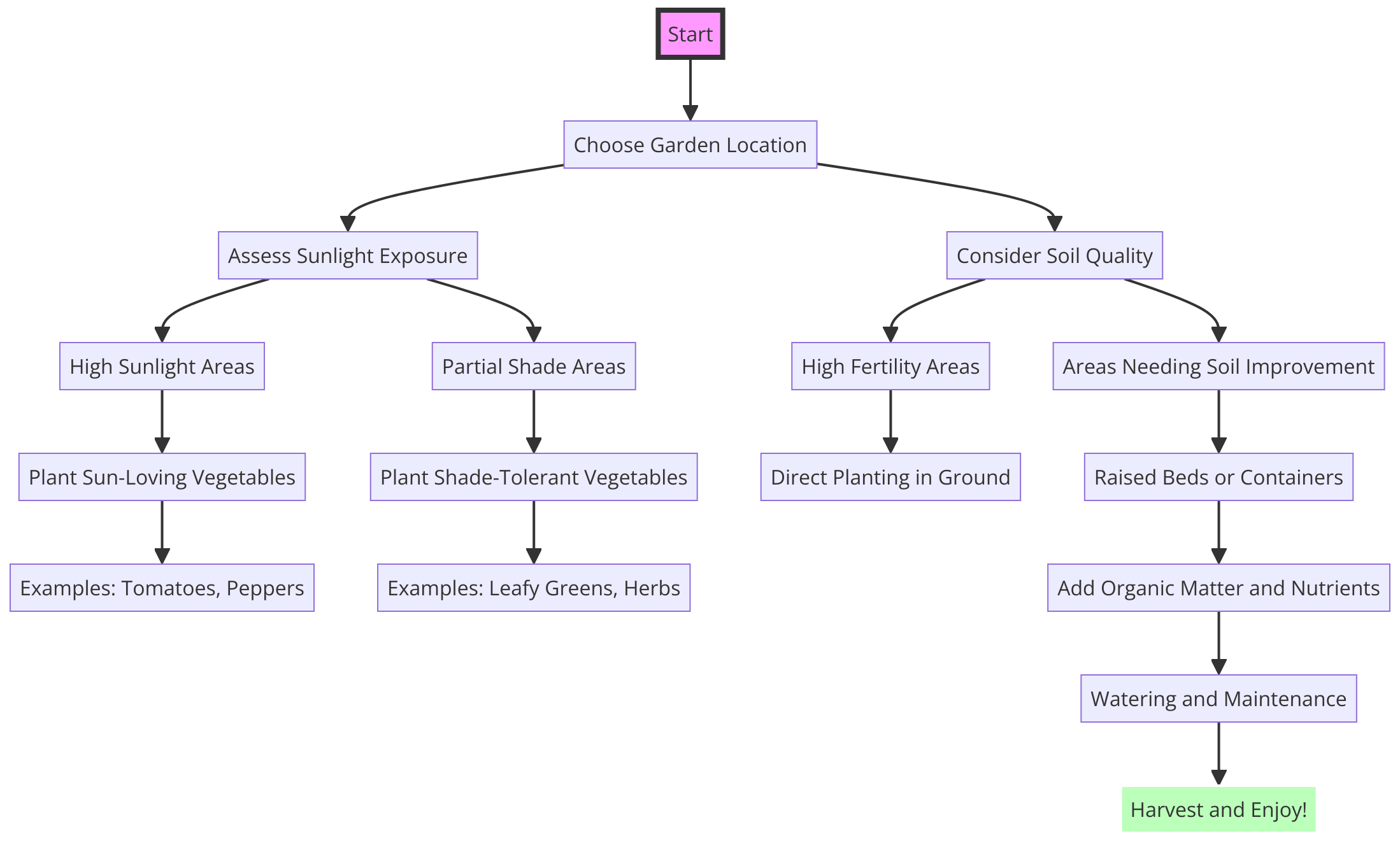
Designing Your Survival Garden Layout for Maximum Yield

Importance of Efficient Layout
When planning your best survival garden, it’s essential to consider the layout for maximum yield.
Embrace vertical gardening to extend your growing season and make the most of limited space.
With vertical structures, you not only grow vegetables but can also grow useful plants like potatoes which take up minimal ground space.
Incorporating Diversity
Diversify the layout of your garden to learn how to grow a variety of plants effectively.
Incorporate different sections for various growing a garden necessities; dedicate specific areas for grow plants that thrive in shaded spots and others basking in sunlight.
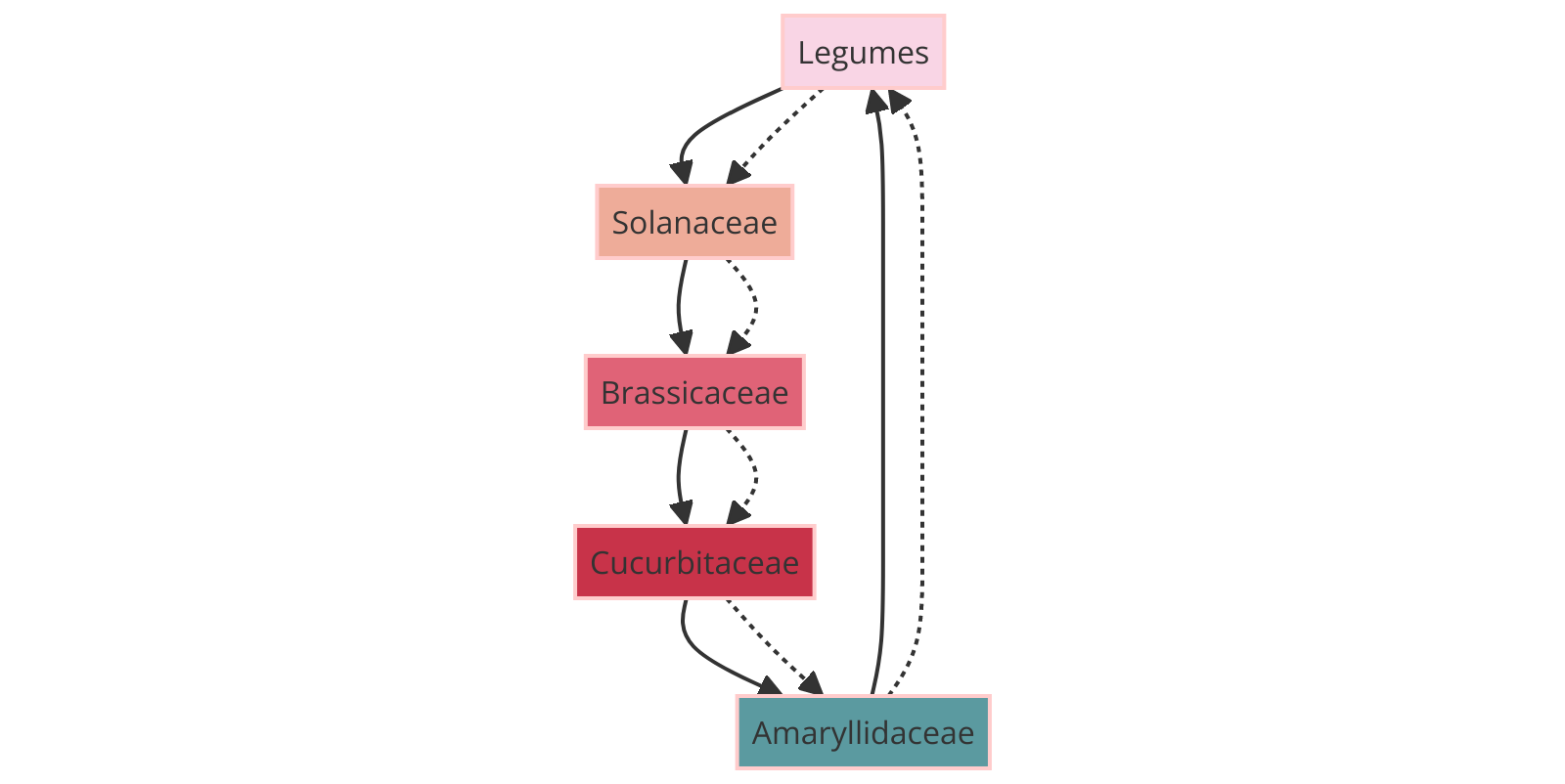
By creating a well-thought-out plan for your garden layout, you can also grow complementary crops that support each other’s growth.
| Benefits of Plant Variety | Description |
|---|---|
| Nutrient Availability | Varied crop nutrient requirements prevent depletion and some fix nitrogen |
| Pest Management | Diverse plantings disrupt pest cycles, companion planting reduces pesticide needs |
| Soil Health Improvements | Crop rotation prevents erosion, deep roots improve soil structure, legumes fix nitrogen |
“Diversity in a survival garden isn’t just about the variety of crops; it’s about creating a resilient ecosystem that supports itself,”
reflects Sofia Patel, ecologist and gardener
Best Survival Garden Practices: From Soil to Harvest

Planning Your Survival Garden
When planning your survival garden, it’s crucial to consider the amount of food you aim to produce based on the growing space available.
Whether you have a small garden or a more common garden, having a garden plan can help ensure a productive survival garden.
For those new to gardening, selecting garden seeds that are suitable for survival food can be a great starting point.
Remember to also think about the growing conditions outside the garden to optimize the success of your crops.
Optimizing Growing Conditions for Maximum Yield
Creating a productive garden involves maximizing the growing space you have.
Pay attention to the type of soil you have and invest time in enriching it to grow much as possible.
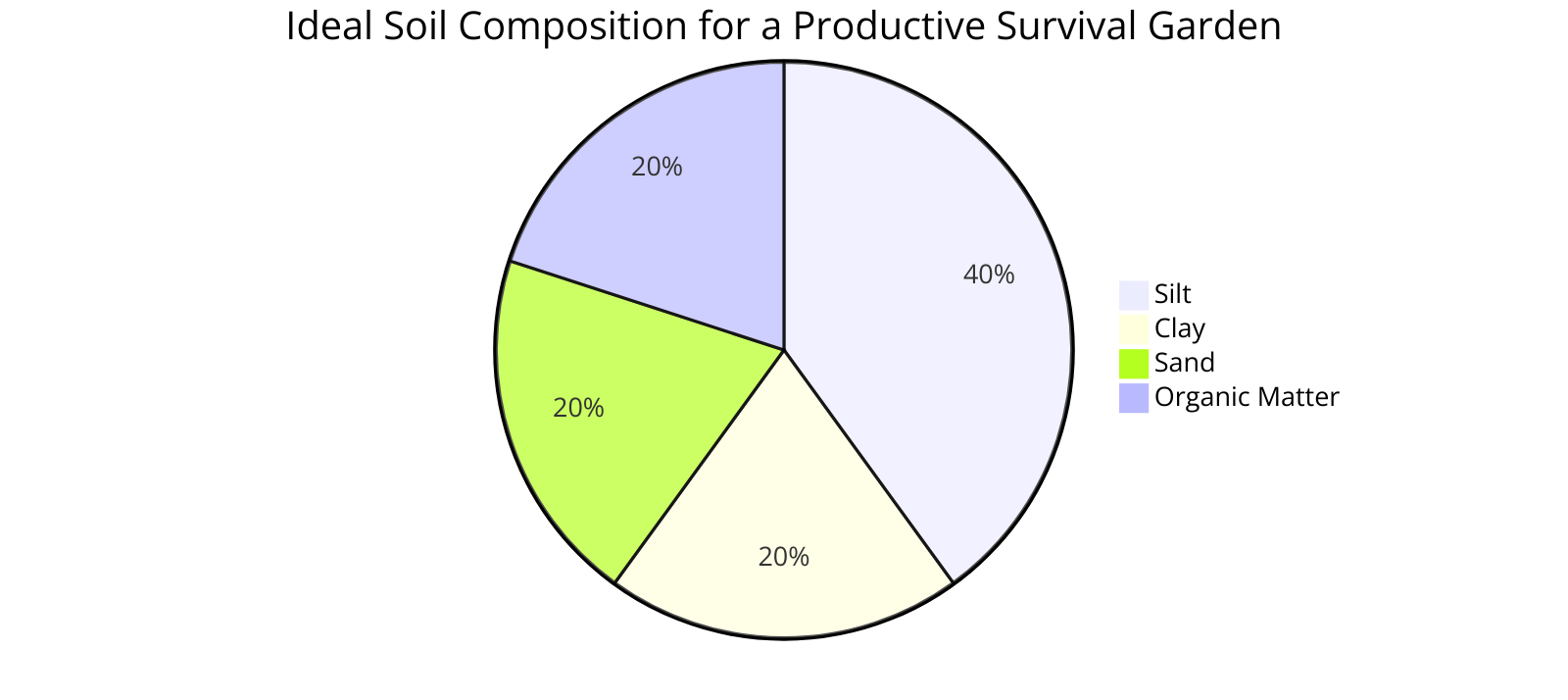
Consider companion planting to make the most out of your garden for survival and ensure that your plants have the necessary support to thrive.
| Pest | Companion Plants | Natural Remedies |
|---|---|---|
| Aphids | Nasturtiums, Marigolds | Insecticidal soap, neem oil, ladybugs, garlic spray |
| Cabbage Worms | Sage, Dill, Mint | Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt), handpicking, row covers |
| Slugs and Snails | Thyme, Lavender, Rosemary | Copper barriers, diatomaceous earth, beer traps |
| Tomato Hornworms | Borage, Marigolds | Handpicking, attract beneficial insects like parasitic wasps |
| Whiteflies | Basil, Nasturtiums | Yellow sticky traps, reflective mulches, insecticidal soap |
| Carrot Flies | Rosemary, Sage | Floating row covers, crop rotation, companion planting |
| Cucumber Beetles | Radishes, Nasturtiums | Kaolin clay, diatomaceous earth, beneficial nematodes |
| Japanese Beetles | Garlic, Catnip | Handpicking, pheromone traps, neem oil spray |
Regularly monitor the health of your crops and be prepared to make adjustments to your care routine.
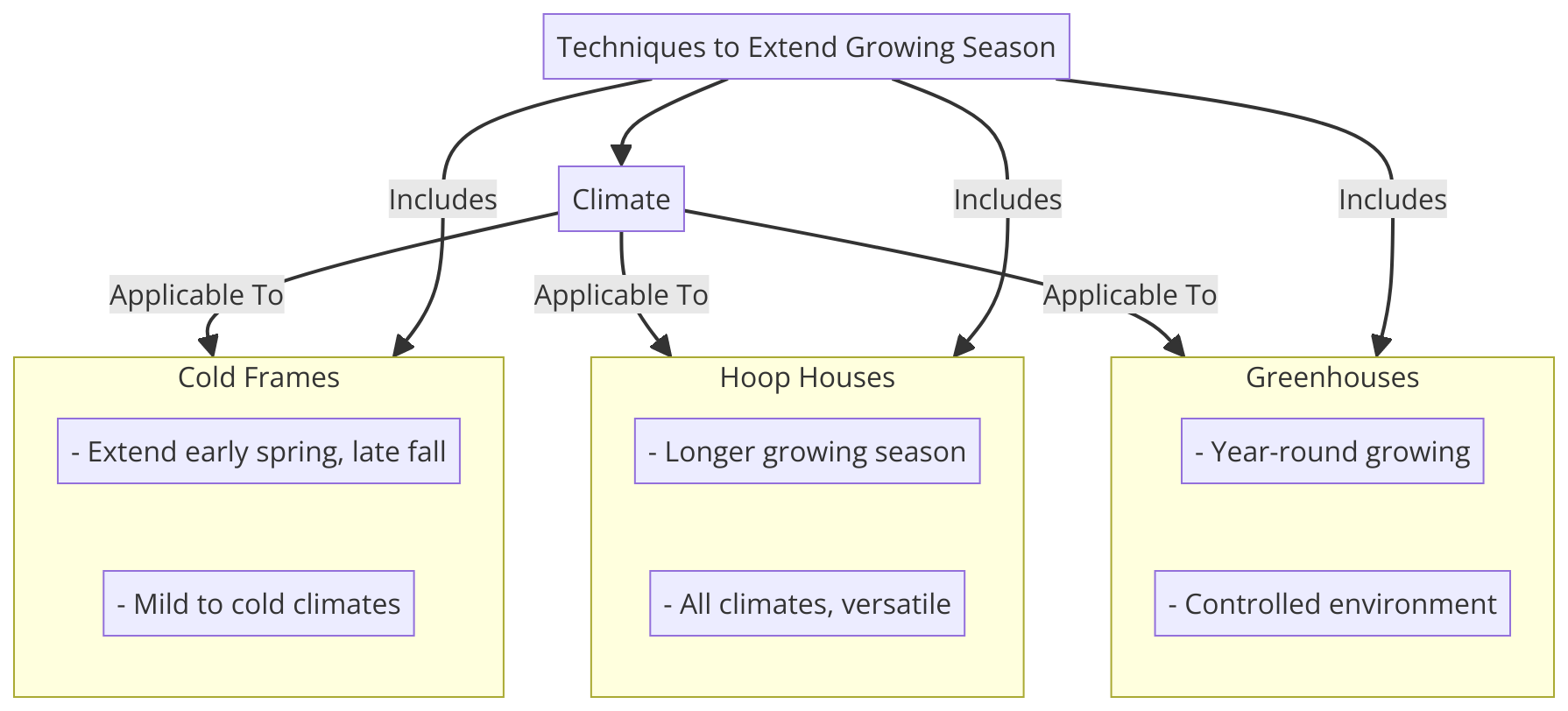
How to Plant a Survival Garden: Techniques and Timing

Timing Is Key
When planting your survival garden, it’s crucial to consider the right timing to grow crops effectively.
Different plants have specific seasons for planting to thrive and become survival garden staples.
By understanding the optimal planting times, you ensure the health of your garden and maximize the yield your survival garden can provide.
Extending Your Harvest
To eat what you grow and extend the growing season, consider planting a mix of cold-season and warm-season crops in your garden to survive.
| Crop | Cold-Hardy/Heat-Tolerant | Growth Habit | Harvest Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cold-Hardy | |||
| Kale | Cold-hardy | Leafy greens | 50-70 days |
| Spinach | Cold-hardy | Leafy greens | 30-45 days |
| Carrots | Cold-hardy | Root vegetables | 70-80 days |
| Broccoli | Cold-hardy | Brassica | 60-100 days |
| Brussels Sprouts | Cold-hardy | Brassica | 90-110 days |
| —————— | ————————— | ————————- | ———————- |
| Heat-Tolerant | |||
| Tomatoes | Heat-tolerant | Fruit-bearing | 60-100 days |
| Peppers | Heat-tolerant | Fruit-bearing | 60-90 days |
| Cucumbers | Heat-tolerant | Vine vegetables | 50-70 days |
| Okra | Heat-tolerant | Pod vegetable | 50-65 days |
| Eggplant | Heat-tolerant | Fruit-bearing | 60-80 days |
Include vegetables and fruits that grow in a survival garden and are easy to grow and store.
Plant people like to grow as well as those you want your garden for a well-rounded survival garden.
Consider techniques like intercropping and companion planting to maximize space and resources.
Survival Garden Care: Maintaining Your Food Source

Starting Small and Growing: A Key Strategy
When planning a survival garden, remember that it’s crucial to start small and grow.
Begin by selecting a few great survival crops that thrive in your region.
Square-foot gardening or herb gardening can be excellent ways to maximize your space and yield.
Consider the following tips to design a survival garden to feed your family:
- Choose survival garden crops that are suitable for your climate and growing conditions.
- Opt for garden plants that are low-maintenance and able to grow well together.
- Implement regular watering and weeding routines to ensure your plants stay healthy.
Sustainable Growth for Sustenance
Maintaining a survival garden involves ongoing care and attention to optimize your harvest.
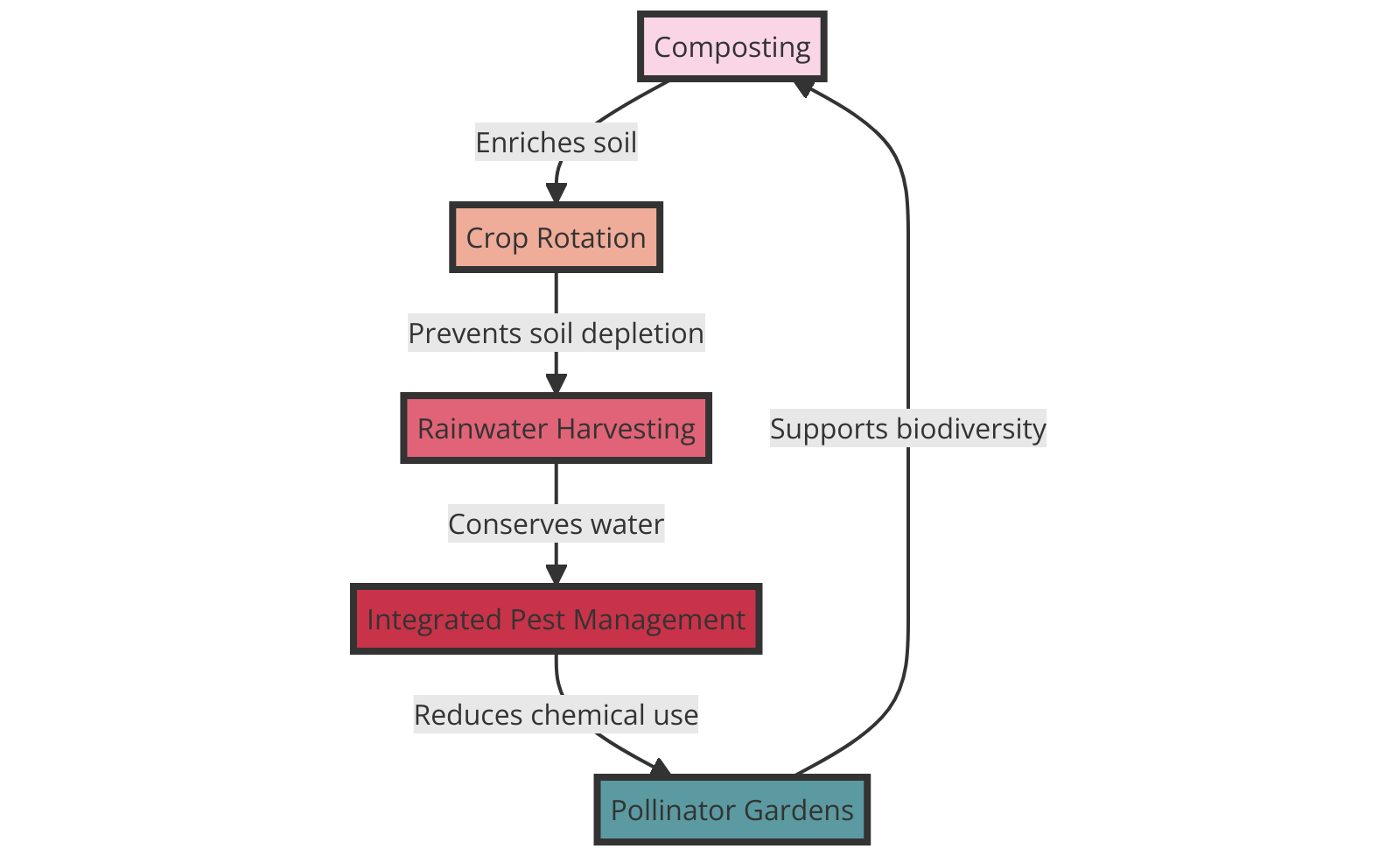
Despite your best efforts, challenges like pests or weather fluctuations may arise. Here are practical steps for survival garden care:
- Keep a close eye on your plants’ health and address any issues promptly.
- Mulch your garden beds to retain moisture and deter weeds.
- Practice companion planting to naturally repel pests and boost plant growth.
| Technique | Water Use | Soil Health | Yield |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Gardening | Often high water use, | Soil may become depleted | Yield may vary depending |
| especially with | of nutrients over time, | on external factors such | |
| conventional irrigation | leading to decreased fertility, | as weather conditions | |
| methods | compaction, and erosion | ||
| ———————— | ————————- | ——————————– | ————————- |
| Sustainable Gardening | Utilizes water-saving | Emphasizes soil health through | Generally sustainable |
| techniques like drip | practices such as crop rotation, | yields due to improved | |
| irrigation, mulching, | cover cropping, and organic | soil health and natural | |
| and rainwater harvesting | amendments, fostering a | pest control methods | |
| thriving ecosystem |
Harvesting Your Garden Crops: Timing and Techniques for Best Yield

Knowing the Right Time to Harvest
In a successful survival garden, timing is crucial.
Make sure to refer back to your survival garden plan to understand when each crop should be harvested.
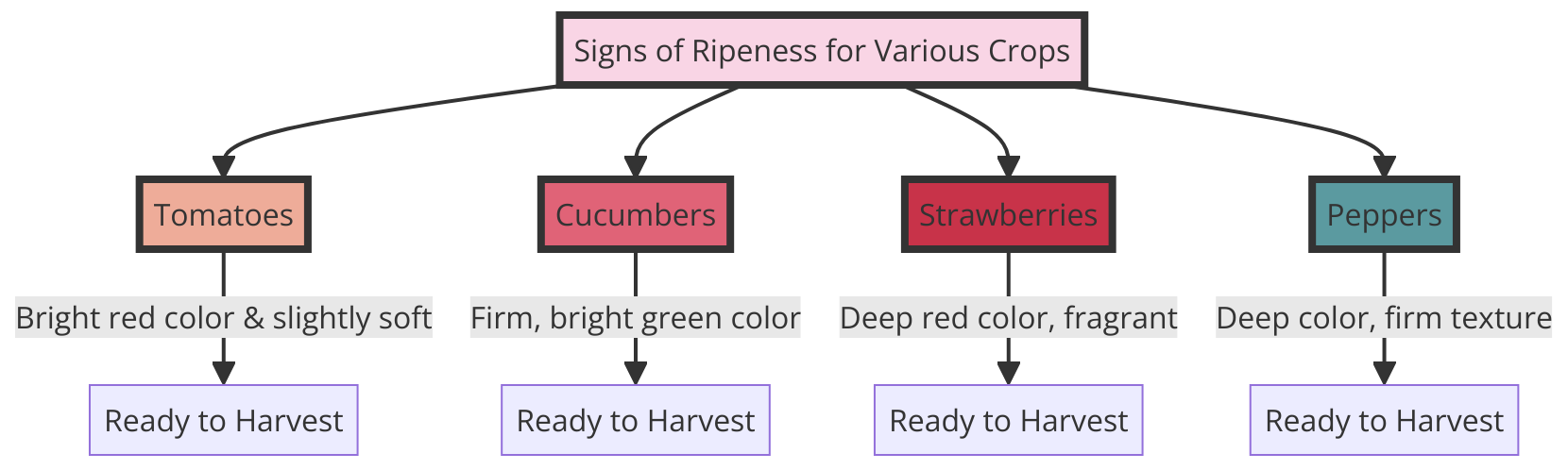
Remember, not all vegetables mature at the same pace, so being aware of the length of your growing season is essential.
Your garden design should take into account the time to grow each crop to ensure a continuous supply of fresh produce.
Implementing Proper Harvesting Techniques
When it comes to harvesting, gentle handling is key to preserving the quality of your produce.
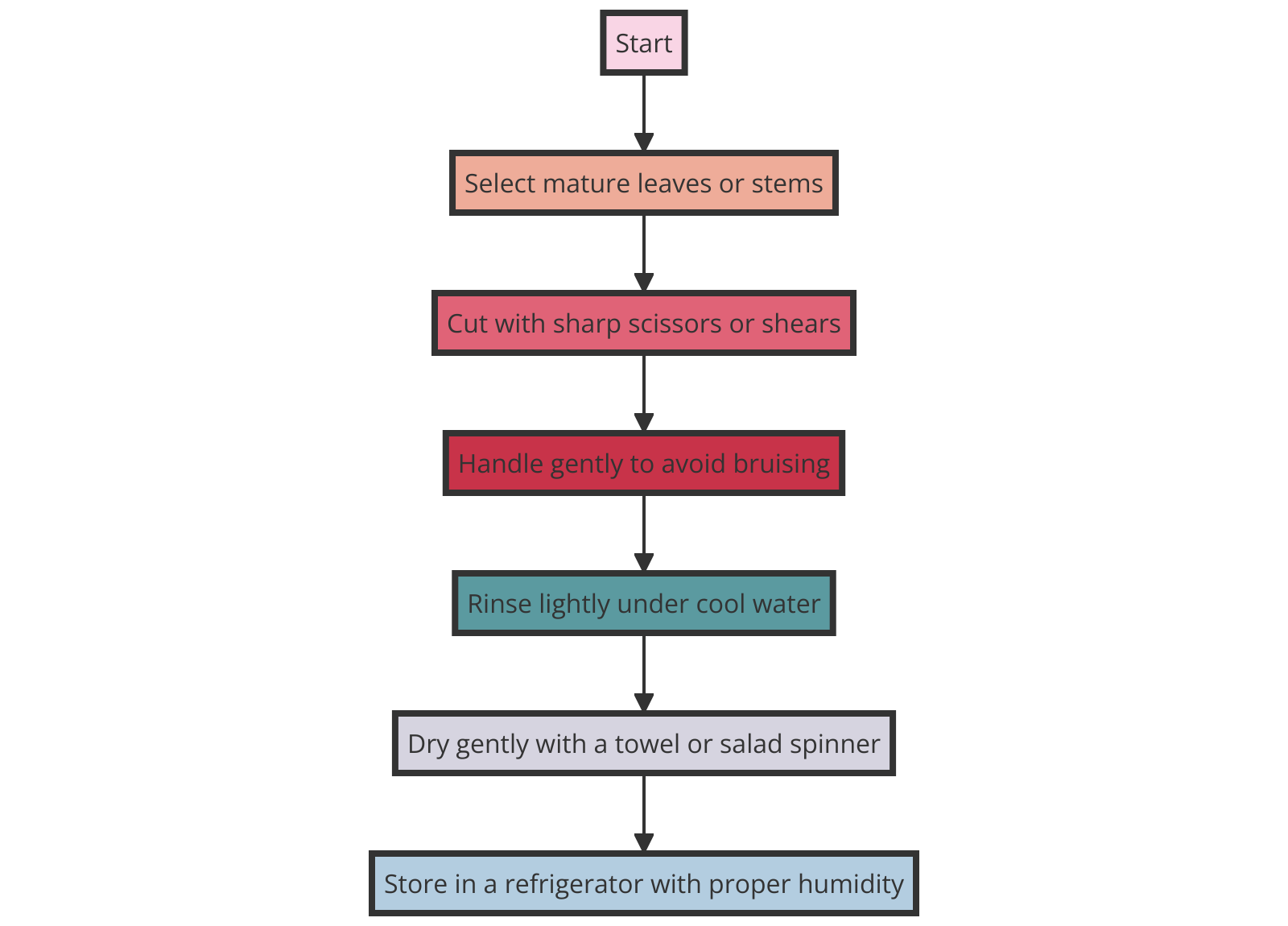
For crops that are harder to grow, such as delicate herbs or fruits, ensure you use sharp, clean tools to avoid damaging the plant.
For leafy greens, harvest in the early morning for the best flavor and texture.
| Harvest Type | Best Storage Method |
|---|---|
| Root Vegetables | Cool, dark place with high humidity (root cellar, fridge) |
| Leafy Greens | Wrapped in paper towels in airtight container (fridge) |
| Tomatoes | Room temperature, away from sunlight (countertop) |
| Berries | Single layer on paper towel-lined tray (fridge) |
| Citrus Fruits | Room temperature or fridge crisper drawer |
| Potatoes | Cool, dark place with good ventilation (paper bag, basket) |
| Onions | Cool, dry, well-ventilated place (mesh bag, cool cellar) |
Your garden gives back what you put into it, so treat your plants with care during harvest time.
Remember, a well-planned approach to harvesting not only ensures the best yield, but also promotes the health and longevity of your garden for future harvests.
More Resources:
- Epic Gardening provides a detailed list of the 20 best crops for a survival garden, highlighting the importance of choosing calorie-dense and easy-to-grow varieties like potatoes and kale. Visit Epic Gardening for more insights.
- Gardener’s Path offers comprehensive advice on planning a survival garden, emphasizing the importance of considering your USDA Hardiness Zone and selecting both annuals and perennials that offer nutritional value and storage potential. Learn more at Gardener’s Path.
- Off Grid World discusses the critical steps in growing a survival garden, including selecting the ideal location, considering climate zones, and choosing nutritionally dense foods. Find detailed guidance at Off Grid World.
- Morning Chores outlines everything you need to know to get started with a survival garden, from choosing crops that store well to the importance of saving seeds for future planting. Visit Morning Chores for detailed strategies and tips.
- For those interested in a comprehensive guide to the healing properties of herbs and other plants in a survival garden, visit The Micro Gardener.





